Cognitive Computing And Healthcare

The Cognitive Era
This is the era of Cognitive Computing, a concept which involves systems or processes which ingest a lot of data related to an area of interest and use that to provide context-sensitive intelligent answers to questions related to that area.
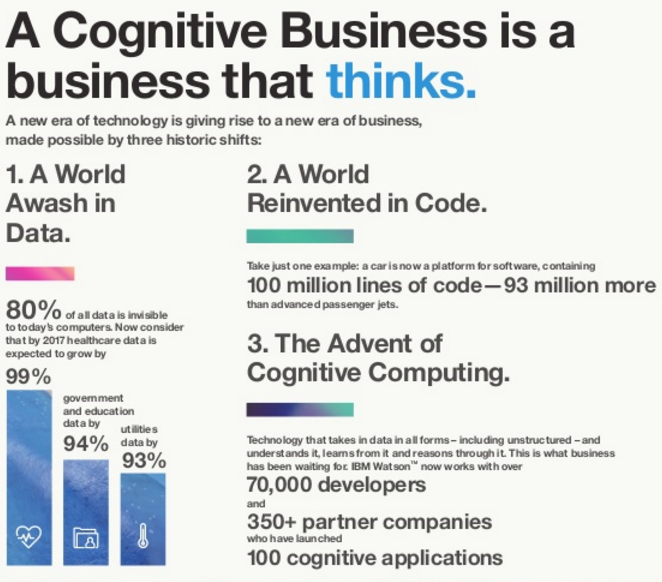
The world is awash with data. 90% of world’s data was created in the last two years. 80% of that data is unstructured. Cognitive systems ingest this data, understand it, learn from it and reason through it. They are able to provide answers to complex queries with this data. The possibilities which such platforms enable are only limited by human imagination.
Watson is a new computing platform (a supercomputer, by some definitions) from IBM that embodies the new Cognitive Era. It has the ability to absorb monumental amounts of data, synthesize it, and help solve some of the world’s most complex problems, including healthcare.
Cognitive Era and Healthcare
India has less than 2000 oncologists (doctors who treat cancer). Whereas India is witnessing an epidemic of cancer. Such is the shortage of oncologists, that Manipal Hospital at Goa took 7 months to convince an oncologist to come on board. Most remote locations of India do not have oncologists or even access to them. India has limited specialized oncology centres, where there is hope to treat cancer, the killer disease. Most cancer patients in India, sadly, just die, as they have little to no recourse to get any chance of treatment. Upmarket patients may get some access to the limited cancer hospitals around India.
Manipal Hospital is the first private customer of IBM Watson in India. Dr Ajay Bakshi, CEO of Manipal Hospitals, is a former McKinsey consultant and a neurosurgeon. He led the launch of Watson at Manipal Hospital’s oncology department. Watson will allow his oncologists, who were severely overwhelmed by the deluge of cancer patients until recently, to have a multiplier effect. Dr Bakshi of Manipal says that Watson is like hiring a genius assistant for their oncologists to assist in diagnosis and treatment of cancer, albeit an expensive assistant (as Watson is quite expensive).
Watson for Oncology combines patient’s data, both structured and unstructured, with the vast research material it already has and computes evidence-based treatment options for the patient. This is the power of Cognitive computing.
Hiring new oncologists is a nightmare as there are not that many out there. So Watson is the only hope for Manipal to multiply limited cancer diagnostic capability. It also allows remote diagnosis of critical disease as specialists like oncologists are not available everywhere. A local surgeon can collaborate with an oncologist in another location and help treat cancer with Watson’s support.
Health is the biggest vertical for IBM Watson, so much so that IBM has created a special division called Watson Health, whose charter is to deploy Watson in healthcare facilities around the world and train the medical community to leverage the Cognitive abilities of Watson. Watson is a resident doctor (well, almost) in 14 top oncology centres in the world., Manipal Hospital in India being the latest one.
Watson has global aggregate data on healthcare, especially in oncology. IBM choose oncology as key focus area initially, as this is something where a lot of data analysis is involved and global aggregation of data makes the analysis more valuable with time. Watson learns from everything that is fed to it and applies those learnings to future prognosis that it renders. This is an example of Cognitive computing.
Another use of Watson is in pharma research, where it takes typically years to research and release drugs, and involves reams of data and years of clinical trials to check on drug effectiveness. Watson can lower time frames needed for drug research and clinical trials (Cognitive Exploration).
Manipal Hospital is discussing a project with IBM to use Watson to digitize India’s 1.2 billion people health records. And use that data for public health outbreak predictions. The challenge of predicting public health outbreaks like Dengue or Zika virus require analysis of massive no of data points and is classic use case for Watson’s Cognitive abilities.
Each human being will generate 1 million GB of health-related data in their lifetime. This is equivalent of 300 million books. One definitely needs supercomputing tech to make sense of this.
Over time, Watson will apply Cognitive analysis for other areas of healthcare, as it continues to ingest more data on a wide variety of health domains.