Signs, Tests And Treatments Of Kidney Stone!

Symptoms of kidney stone:
Kidney stones form in the kidney. If they stay in the kidney then they generally do not cause pain. When they travel out of the body through the tubes of the urinary tract their movement may cause:
- No symptoms if the stone is small
- Feeling sick to stomach and vomiting
- Blood in the urine (hematuria), which can occur either with stones that stay in the kidney or with those that travel through the ureters.
- Frequent and painful urination which may occur when the stone is in the ureter or after the stone has left the bladder and is in the urethra. Painful urination may occur when a urinary tract information is present.
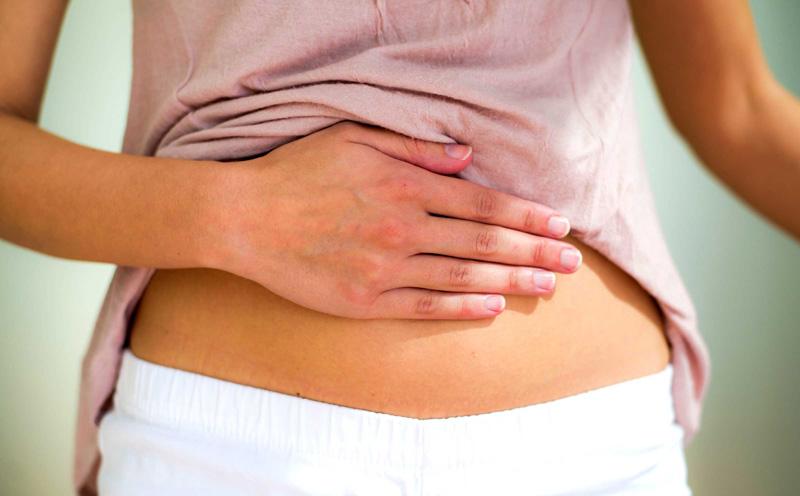
- Sudden, severe pain that gets worse in waves. Stones may cause intense pain in the back, side, abdomen, groin, or genitals. People who have had a kidney stone often describe the pain as “the worst pain I’ve ever had.”
- blood in the urine (red, pink, or brown urine)
- nausea
- discolored or foul-smelling urine
- fever
- frequent need to urinate
- Urinating small amounts of urine
Tests and Treatments
The following tests can rule out obstruction:
- Abdominal X-rays
- Intravenous Pyelogram (IVP)
- Retrograde Pyelogram
- Ultrasound of the kidney (this is the preferred study)
- MRI of the abdomen and kidneys
- Abdominal CT scan
Treatment is tailored according to the type of stone. Urine can be strained and stones collected for evaluation. Drinking six to eight glasses of water a day increases urine flow. People who are dehydrated or have severe nausea and vomiting may need intravenous fluids.
Other treatment options include:
Medication
Pain relief may require narcotic medications. The presence of infection requires treatment with antibiotics. Other medications include:
- Allopurinol for uric acid stones
- Diuretics
- Sodium bicarbonate or sodium Citrate
- Phosphorus solutions